Enzyme biofactories to enhance cord blood transplants
21 October, 2020
A new way of producing an enzyme called fucosyltransferase VI (FTVI) in the lab could help enhance the therapeutic potential of cord blood transplants.
Cord blood is currently used to treat more than 80 life-threatening conditions, ranging from cancer and immune deficiency to metabolic and genetic disorders. The therapy is predicated on the idea that stem cells in the cord blood will traffic to the bone marrow, where they can help rebuild a healthy blood and immune system that has been damaged by disease. But cord blood stem cells are not naturally adept at this process—which is why several drugmakers have turned to FTVI as a way of enhancing the cells’ homing ability.
Click here to read the full story
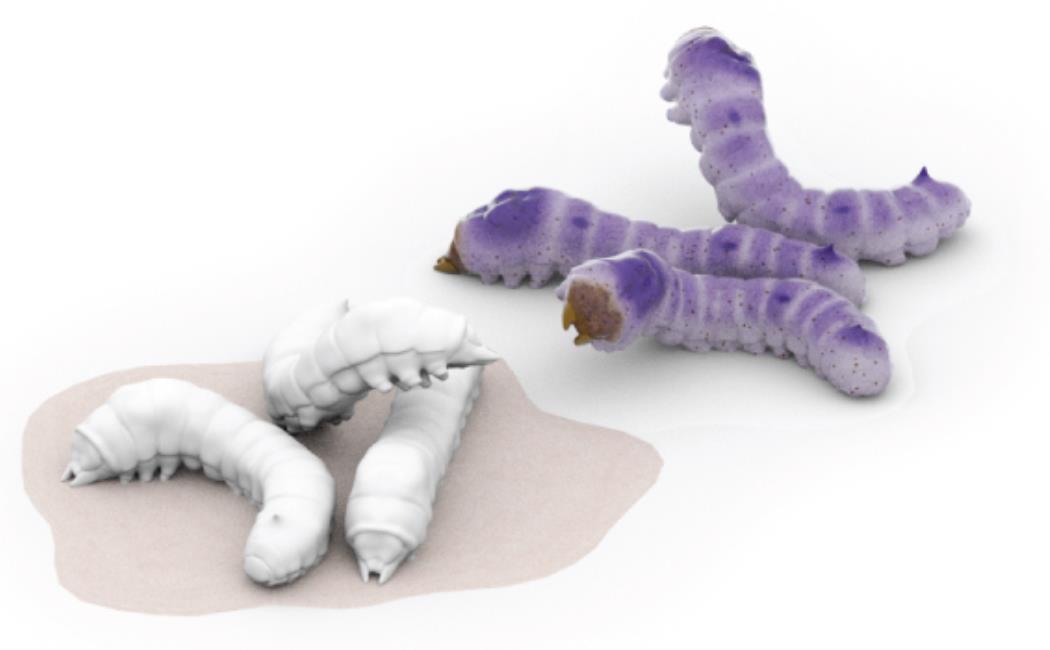
Image: The researchers showed that their yeast- and silkworm-derived enzyme far outperformed commercial sources of the enzyme made in standard expression systems.
© 2020 KAUST; Heno Hwang