Coral symbionts have a genome like no other
29 April, 2021
The genome of single-celled plankton, known as dinoflagellates, is organized in an incredibly strange and unusual way, according to new research. The findings lay the groundwork for further investigation into these important marine organisms and dramatically expand our picture of what a eukaryotic genome can look like.
Researchers from KAUST, the U.S. and Germany have investigated the genomic organization of the coral-symbiont dinoflagellate Symbiodinium microadriaticum. The S. microadriaticum genome had already been sequenced and assembled into segments known as scaffolds but lacked a chromosome-level assembly.
The team used a technique known as Hi-C to detect interactions in the dinoflagellate’s chromatin, the combination of DNA and protein that makes up a chromosome. By analyzing these interactions, they could figure out how the scaffolds were connected together into chromosomes, giving them a view into the spatial and structural organization of the genome.
Click here to read the full story.
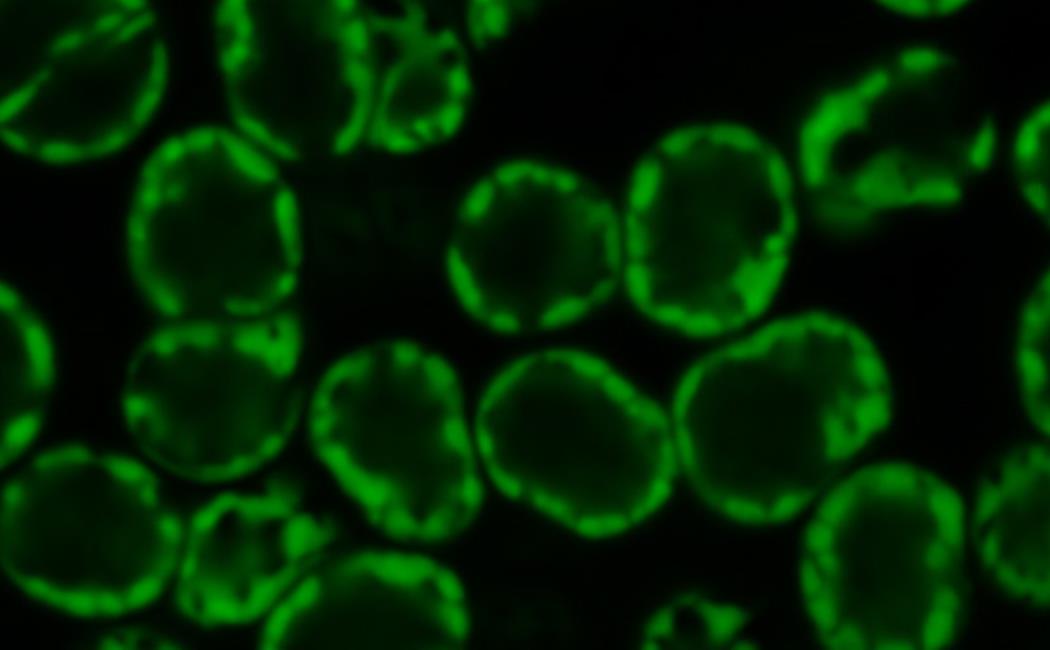
Image: The international research team discovered that the genome of dinoflagellates is organized in a unique way compared to other eukaryotic genomes.
© 2021 KAUST