Hydrogen storage solution could lie in lakes
02 November, 2024
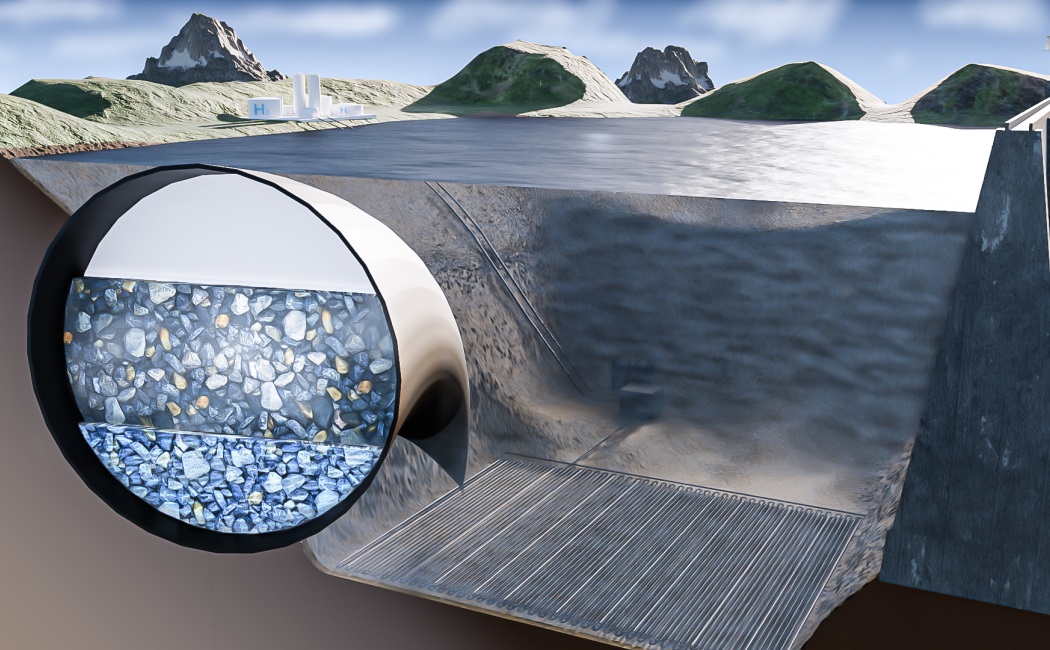
Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel that could help to reduce fossil fuel consumption, but the flammable gas can be challenging to store. KAUST researchers have now calculated that vast amounts of hydrogen could be inexpensively stockpiled in pipes at the bottom of lakes and reservoirs, potentially boosting hydrogen’s role in tackling climate change.
Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind are intermittent, so any excess electricity output must be saved to fill gaps in supply. This can be achieved by powering electrolyzers that split water into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen can be kept until it is needed and then fed into fuel cells to regenerate electricity; the only waste product produced is water.