How a multitasking protein keeps the body's clock in sync
19 January, 2025
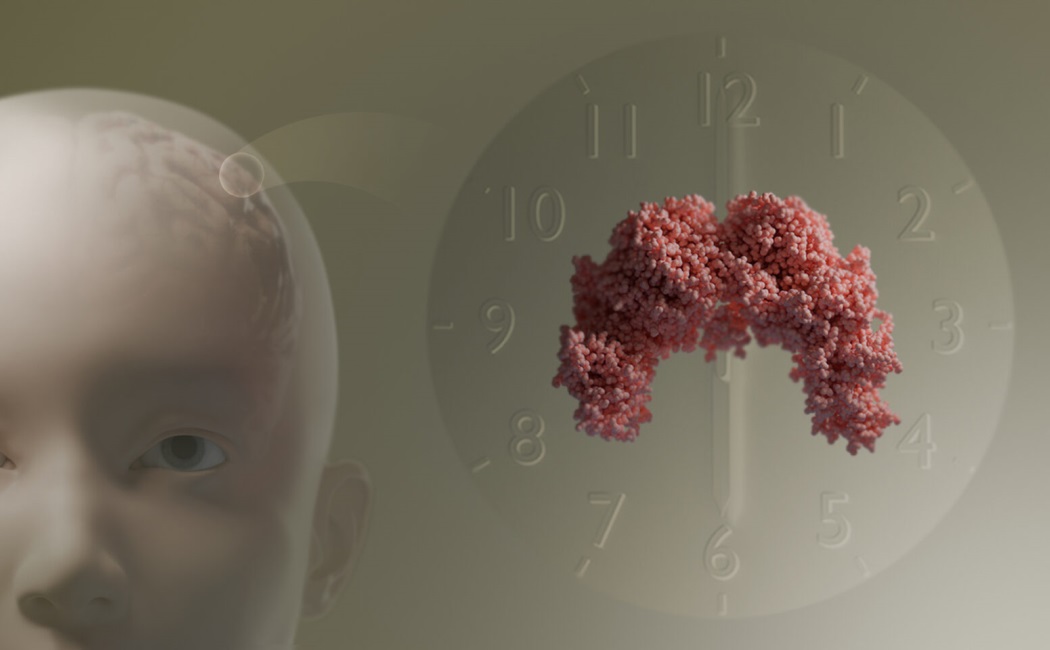
If your genes could set an alarm clock, EZH1 might be the one ringing the bell.
A new study has revealed how this underappreciated protein ensures the rhythmic expression of genes in skeletal muscle, aligning them with the body’s 24-hour internal cycle.
A KAUST-led research team showed that EZH1 plays a dual role in circadian regulation. It both stabilizes a critical protein called RNA Polymerase II — the molecular engine of gene transcription — and reshapes the structure of chromatin, the tightly packed form of DNA, to activate or silence genes on schedule.